Health Vs Life Insurance Key Differences
Health vs Life Insurance: Key Differences delves into the crucial distinctions between these two vital financial safeguards. Understanding their unique coverage, costs, and considerations is essential for informed decision-making. Health insurance focuses on medical expenses, while life insurance provides financial protection for loved ones upon your passing. This exploration clarifies the nuances of each type, empowering readers to choose the best options for their specific needs.
This comprehensive guide will navigate the complexities of both types of insurance, from understanding their fundamental purposes to exploring the various factors influencing premium costs. We will compare and contrast coverage options, outlining situations where one type of insurance might be more beneficial than the other. By the end, you will have a clearer understanding of how to select and purchase the appropriate insurance plan.
Introduction to Insurance
Insurance products are designed to protect individuals and businesses from financial losses arising from unforeseen events. By pooling risk among many participants, insurance allows for the sharing of potential losses, making them more manageable for all involved. This mechanism ensures that individuals and entities can maintain financial stability even when faced with substantial unexpected costs.A key aspect of insurance is the transfer of risk.
Rather than bearing the entire financial burden of a potential loss, individuals or businesses transfer that risk to an insurance company. In return for regular payments called premiums, the insurance company agrees to compensate for losses up to a certain limit, as Artikeld in the policy terms. This transfer of risk provides peace of mind and allows for more effective financial planning.
Common Types of Insurance
Insurance products are diverse, catering to a wide array of needs. The most common types include health insurance, life insurance, property insurance, auto insurance, and liability insurance. Each type of insurance addresses specific potential risks and financial consequences.
Health Insurance vs. Life Insurance
Health insurance protects individuals from the financial burden of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, and treatments. It ensures access to necessary medical care without being financially crippled by the associated costs. Life insurance, on the other hand, provides a financial safety net for beneficiaries in the event of the insured person’s death. It safeguards their loved ones from financial hardship by providing a lump-sum payment.
The fundamental difference lies in the circumstances covered and the intended beneficiaries.
Key Differences Between Insurance Types
The following table highlights the key distinctions between various insurance types, emphasizing the different risks covered and the nature of the compensation provided:
| Insurance Type | Coverage | Compensation | Beneficiaries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Health Insurance | Medical expenses (doctor visits, hospital stays, treatments) | Reimbursement for medical costs up to policy limits | Policyholder (and often dependents) |
| Life Insurance | Death of the insured | Payment of a lump sum to beneficiaries | Designated beneficiaries |
| Property Insurance | Damage or loss of property (home, car, etc.) due to perils like fire, theft, or natural disasters | Reimbursement for the damage or replacement cost of the property | Policyholder |
| Auto Insurance | Vehicle damage or injury to others in an accident | Reimbursement for vehicle damage, medical expenses of others, and potential legal liabilities | Policyholder and others involved in the accident |
| Liability Insurance | Legal liability for injuries or damages caused to others | Compensation for damages and legal fees arising from the policyholder’s liability | Injured parties and legal entities |
Health Insurance
Health insurance plays a crucial role in protecting individuals and families from the financial burden of unexpected medical expenses. It provides a safety net, allowing individuals to access necessary medical care without facing catastrophic out-of-pocket costs. Understanding the various aspects of health insurance policies is essential for making informed decisions about coverage and affordability.A typical health insurance policy offers a range of benefits designed to cover a variety of medical needs.
These benefits often include preventive care services, such as routine check-ups and immunizations, as well as coverage for hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription medications. Policies typically vary in the extent of coverage, with some providing more comprehensive care than others.
Essential Benefits Covered
Health insurance policies generally cover a broad spectrum of medical expenses. Essential benefits frequently include: emergency room visits, hospitalization, physician services, maternity care, mental health services, and prescription drugs. The specific details and extent of coverage may differ among policies.
Common Exclusions
Not all medical expenses are covered by health insurance policies. Common exclusions often include: pre-existing conditions (though some policies may offer coverage after a waiting period), cosmetic procedures, experimental treatments, and certain alternative therapies. It is critical to review the specific policy document to understand the full scope of exclusions.
Deductibles, Co-pays, and Co-insurance
These cost-sharing mechanisms are important components of health insurance plans. Deductibles represent the amount an individual must pay out-of-pocket before the insurance company begins to contribute. Co-pays are fixed fees for specific services, like doctor visits or prescription drugs. Co-insurance refers to the percentage of medical costs that the insured party is responsible for after meeting the deductible.
Understanding these components is vital for estimating the total cost of care.
Types of Health Insurance Plans
Several types of health insurance plans are available, each with its own features and characteristics. The most common types include:
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): HMOs typically require members to choose a primary care physician (PCP) within their network. This PCP coordinates care and refers patients to specialists within the network. Generally, out-of-network care is limited or not covered, except in emergencies. HMOs usually have lower premiums than other plans, but patients may have limited choice in providers.
- Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs): PPOs allow members to choose any provider, in-network or out-of-network. While out-of-network care is often available, it is typically more expensive. PPOs offer greater flexibility in choosing providers but often have higher premiums than HMOs.
- Point-of-Service (POS) Plans: POS plans combine elements of HMOs and PPOs. Members select a PCP and can use in-network providers without a referral. However, using out-of-network providers typically requires a higher cost-sharing arrangement.
Typical Costs Associated with Different Plans
The cost of health insurance varies significantly depending on factors such as plan type, coverage level, and location. The following table provides a general overview of the typical costs associated with different health insurance options:
| Plan Type | Premium (Estimated) | Deductible (Estimated) | Co-pay (Estimated) | Co-insurance (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HMO | $300-$600 per month | $1,500-$3,000 | $25-$50 per visit | 10%-20% |
| PPO | $400-$800 per month | $2,000-$5,000 | $25-$50 per visit | 20%-30% |
| POS | $350-$700 per month | $1,800-$4,000 | $25-$50 per visit | 15%-25% |
Note: These are estimated costs and may vary significantly based on individual circumstances and specific plan details.
Life Insurance
Life insurance provides a financial safety net for loved ones in the event of the policyholder’s death. It’s a crucial tool for protecting dependents and ensuring financial security during challenging times. Understanding the different types of policies, premium calculations, and payout options is essential for making informed decisions.
Types of Life Insurance Policies
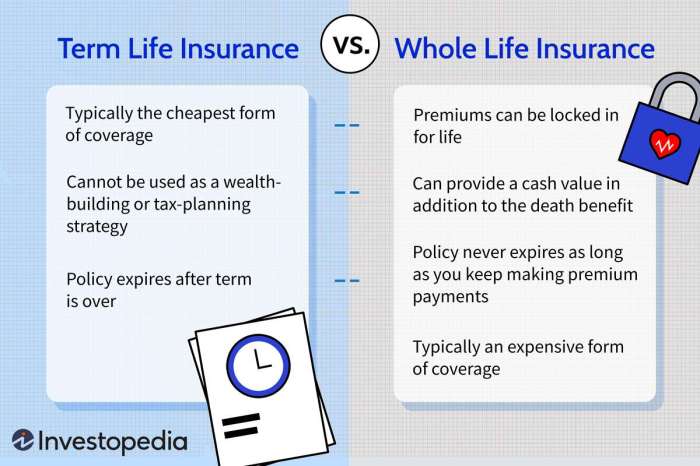
Various life insurance policies cater to different needs and financial situations. The most common types include term life insurance and whole life insurance. Term life insurance offers coverage for a specific period, while whole life insurance provides lifelong coverage.
- Term Life Insurance: This type of policy provides coverage for a predetermined period, typically ranging from 10 to 30 years. Premiums are generally lower compared to whole life insurance, making it an attractive option for those seeking temporary coverage. The coverage expires at the end of the term, unless renewed.
- Whole Life Insurance: This policy provides lifelong coverage and often includes a cash value component. Premiums are typically higher than term life insurance, but the cash value grows over time, potentially offering additional financial benefits. This option is frequently considered for long-term financial security and estate planning.
Premium Calculation
Life insurance premiums are calculated based on various factors. Age, health, lifestyle choices, and the desired coverage amount all play a role in determining the premium. Generally, a younger, healthier individual will pay a lower premium for the same coverage amount. Insurance companies use complex actuarial models to assess risk and calculate premiums accordingly.
Premiums are determined using actuarial models that estimate the probability of death at different ages, and the costs associated with administering the policy.
Payout Options
Life insurance policies offer different payout options. The most common payout is a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries. Other options might include installment payments or a combination of both. The specific payout option is usually Artikeld in the policy document.
- Lump-Sum Payment: This is the most common payout method, where a lump sum of money is paid to the beneficiaries upon the death of the insured.
- Installment Payments: This option provides beneficiaries with regular payments over a specific period, which can be helpful for long-term financial support.
- Combination Payouts: Some policies offer a combination of lump-sum and installment payments, allowing beneficiaries to receive both immediate and ongoing financial assistance.
Reasons for Purchasing Life Insurance
People purchase life insurance for a variety of reasons, primarily to protect their loved ones financially. The primary reasons include providing financial security for dependents, paying off debts, funding education expenses, and ensuring a smooth transition for the family.
- Financial Security for Dependents: Providing for the financial needs of dependents, such as children or a spouse, is a primary motivation for purchasing life insurance. This can cover expenses like housing, education, and daily living costs.
- Debt Repayment: Life insurance can be used to pay off outstanding debts, such as mortgages or loans, preventing financial burdens for beneficiaries.
- Education Funding: Securing funds for children’s education is another significant reason. Life insurance can help cover tuition fees and other educational expenses.
- Estate Planning: Life insurance is a key component of estate planning, ensuring a smooth transition for the family and facilitating the distribution of assets according to the policyholder’s wishes.
Comparison of Life Insurance Types, Health vs Life Insurance: Key Differences
The table below provides a comparative overview of premiums and benefits for different life insurance types. This table is a general guideline, and actual premiums will vary based on individual factors.
| Insurance Type | Premium (Example) | Coverage | Cash Value | Flexibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Term Life | $50-$200 per month | Specified period (e.g., 20 years) | No | Lower premiums, greater flexibility in terms of coverage length |
| Whole Life | $200-$500 per month | Lifelong coverage | Yes (grows over time) | Lifelong coverage, cash value accumulation |
Coverage Differences
Health and life insurance, while both vital financial safeguards, offer distinct protections. Understanding their specific coverage areas is crucial for making informed decisions about your personal and family’s financial security. This section delves into the comparative coverage offered by each type of insurance, highlighting when one might be more suitable than the other, and situations where both are essential.Health insurance focuses primarily on covering medical expenses, while life insurance addresses potential financial losses associated with the death of an insured individual.
This distinction in their core functions translates into different types of situations where each plays a crucial role.
Health Insurance Coverage
Health insurance policies typically cover a wide range of medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, prescription medications, and rehabilitation services. The scope of coverage varies considerably based on the specific plan and the policyholder’s needs. Comprehensive plans usually include preventive care services like checkups and immunizations. Some policies also extend to cover pre-existing conditions, although the extent of coverage may differ.
Crucially, the focus remains on the individual’s well-being and the associated medical costs.
Life Insurance Coverage
Life insurance policies provide a financial payout to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured. The payout amount is typically determined by the policy’s death benefit. This benefit can be crucial for covering outstanding debts, funeral expenses, and ensuring the financial well-being of dependents. Life insurance policies may offer various riders to expand coverage, such as accidental death benefits or critical illness coverage.
Different types of life insurance, like term and whole life, have varying premium costs and coverage durations.
Situations Emphasizing Health Insurance
Health insurance is paramount in situations involving significant medical needs. Consider these examples:
- Chronic illnesses: Individuals with chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or cancer often require ongoing medical care, making health insurance a necessity for managing treatment costs.
- Major surgeries or accidents: Major surgeries or accidents can lead to substantial medical bills. Health insurance helps mitigate these costs, providing a crucial safety net.
- Unexpected illnesses: Sudden illnesses or injuries can require immediate medical attention and substantial treatment costs, highlighting the critical role of health insurance in providing financial support.
Situations Emphasizing Life Insurance
Life insurance is particularly important when the financial implications of death need to be addressed. For example:
- Supporting dependents: When a breadwinner passes away, life insurance ensures the financial stability of their dependents, including children and spouse, by providing a lump-sum payment to cover their needs.
- Paying off debts: Life insurance can be crucial in paying off outstanding debts like mortgages, student loans, or other financial obligations, ensuring a smooth transition for beneficiaries.
- Covering funeral expenses: Life insurance can be used to cover funeral costs, ensuring that loved ones can afford appropriate arrangements without incurring additional financial burdens.
Situations Requiring Both Health and Life Insurance
Many scenarios necessitate both types of insurance for comprehensive financial protection.
- Families with young children: Families with young children face potential medical expenses for routine checkups, vaccinations, and unexpected illnesses. Life insurance safeguards the family’s financial future should the primary caregiver pass away.
- Individuals with pre-existing conditions: Individuals with pre-existing conditions may face higher medical costs. Health insurance provides crucial coverage for these costs, while life insurance can provide a financial safety net for their family if they were to pass away.
- Small business owners: Small business owners often carry a significant financial burden. Health insurance protects their health and well-being, while life insurance safeguards the business’s continuity and financial obligations.
Coverage Scope Comparison
| Insurance Type | Scope of Coverage |
|---|---|
| Health Insurance | Covers medical expenses, including doctor visits, hospital stays, surgeries, and prescription medications. |
| Life Insurance | Provides a lump-sum payment to beneficiaries upon the death of the insured, covering debts, funeral expenses, and financial support for dependents. |
Costs and Considerations
Understanding the costs associated with health and life insurance is crucial for making informed decisions. Insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors, and a thorough understanding of these factors can help you budget effectively and choose the most suitable coverage. This section explores the key elements impacting the cost of both types of insurance, enabling a comparative analysis and highlighting strategies for cost reduction.The cost of insurance is not a fixed amount; it varies significantly based on several factors.
Premiums are determined by actuarial models that analyze risk, which in turn are influenced by demographics, health status, and lifestyle choices. Knowing these factors allows you to make informed decisions about your coverage and financial planning.
Factors Influencing Health Insurance Premiums
Health insurance premiums are influenced by a variety of factors. These factors reflect the inherent risks associated with providing healthcare coverage.
- Age: Younger individuals generally pay lower premiums compared to older individuals. This is because younger people are statistically less likely to require extensive healthcare services. For example, a 25-year-old with no pre-existing conditions will likely pay a lower premium than a 65-year-old with chronic conditions.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing conditions or chronic illnesses typically pay higher premiums. This is because their likelihood of needing extensive medical care is higher. For instance, someone with a history of heart disease might have higher premiums than someone without such a history.
- Location: The cost of healthcare services can vary significantly from one region to another. Premiums in areas with higher healthcare costs tend to be higher. For instance, a policy in a major metropolitan area may have a higher premium compared to a rural area.
- Coverage Choices: The specific benefits and services included in a health insurance plan affect the premium. A plan with more comprehensive coverage will typically have a higher premium than a plan with limited coverage.
- Claims History: Individuals with a history of frequent or costly healthcare claims may face higher premiums. This reflects the increased risk associated with such individuals.
Factors Influencing Life Insurance Premiums
Life insurance premiums are also determined by a range of factors, primarily related to the risk of death within a specific time frame.
- Age: Premiums increase significantly with age. The older a person is, the greater the likelihood of death in the foreseeable future. This is a major factor influencing the cost of a life insurance policy.
- Health Status: Individuals with pre-existing health conditions or unhealthy lifestyles are likely to have higher premiums. A person with a history of smoking or heart disease may face higher premiums than a healthier individual.
- Lifestyle Choices: Lifestyle factors such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or participation in high-risk activities can influence premiums. For example, a smoker will typically pay higher premiums than a non-smoker.
- Coverage Amount: The amount of coverage desired directly affects the premium. A larger sum insured will typically result in a higher premium.
- Policy Type: Different types of life insurance policies, such as term or whole life, have different premium structures. A term policy with a shorter duration typically has a lower premium compared to a whole life policy.
Comparative Analysis of Costs
Health and life insurance costs vary based on individual circumstances. While both types of insurance aim to protect against financial hardship, the factors influencing their costs differ significantly.
| Factor | Health Insurance | Life Insurance |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Risk Covered | Illness and injury | Death |
| Key Cost Driver | Healthcare utilization, age, pre-existing conditions | Age, health, lifestyle, coverage amount |
| Cost Trend | Can increase due to rising healthcare costs | Increases with age and health risks |
Ways to Save Money on Insurance Premiums
Several strategies can help reduce insurance costs. Making conscious choices can have a positive impact on your overall financial well-being.
- Shop Around: Comparing quotes from multiple insurance providers can lead to significant savings. Different insurers offer varying premiums and coverage options, and thorough comparison is crucial.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: Adopting healthy habits such as regular exercise and a balanced diet can positively influence your health status, potentially lowering your insurance premiums.
- Consider Lower Coverage Amounts: Reducing the coverage amount can sometimes result in lower premiums, especially for life insurance. This strategy requires careful consideration of your financial needs and future projections.
- Increase Deductibles: Increasing your deductible can often result in lower premiums. However, this strategy involves accepting a greater financial responsibility for healthcare costs.
- Review Your Needs Regularly: Your insurance needs may change over time. Regularly reviewing your coverage and updating it accordingly is essential to ensure that you have the right level of protection.
Impact of Age, Health, and Lifestyle on Costs
Age, health, and lifestyle directly impact insurance costs. These factors are closely correlated with the risk assessment models employed by insurers.
- Age: Age is a critical factor for both health and life insurance. Higher age usually corresponds to higher premiums due to the increased risk of needing healthcare services or death.
- Health: Health conditions, both pre-existing and chronic, increase the likelihood of high healthcare costs, leading to higher premiums for health insurance. Similarly, health conditions increase the risk of death, resulting in higher life insurance premiums.
- Lifestyle: Lifestyle choices, including smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, and lack of exercise, increase the risk of developing health problems, thereby impacting both health and life insurance premiums.
Insurance Selection and Purchase
Choosing the right insurance plan is a crucial financial decision. Understanding the process, comparing different options, and carefully reviewing policy details are essential steps to protect your financial well-being and ensure you have adequate coverage. Careful consideration of your needs and circumstances will lead to a more informed and effective selection process.
Selecting an Appropriate Health Insurance Plan
Selecting a suitable health insurance plan involves a careful evaluation of your individual needs and circumstances. Factors such as family size, pre-existing conditions, and preferred healthcare providers should be considered. Understanding the various plan types, including HMOs, PPOs, and POS plans, is vital to making an informed choice. Each type offers varying levels of coverage and network access.
Researching and comparing plans from different providers is also critical. Factors like deductibles, co-pays, and out-of-pocket maximums significantly impact the cost of care.
Purchasing a Life Insurance Policy
Purchasing a life insurance policy involves a series of steps. The first step is to determine your coverage needs based on your financial obligations and dependents. Consider the amount of coverage required to replace lost income and meet existing financial commitments. Next, you need to compare different policy types, such as term life insurance and permanent life insurance.
These policies differ in their duration, premium structure, and overall cost. It’s important to understand the different features and benefits offered by each type. Evaluating the reputation and financial stability of insurance companies is crucial. Companies with a strong track record of fulfilling their obligations provide greater peace of mind.
Comparing Insurance Companies
Evaluating different insurance companies is a key part of the selection process. Factors like financial strength ratings, customer service reviews, and claims processing times are important to consider. Companies with strong financial ratings demonstrate their ability to meet their obligations, while positive customer feedback suggests a commitment to customer satisfaction. A company’s reputation for efficient claims processing is vital for a smooth experience when you need coverage.
Investigate different insurance providers to find a reputable and reliable company that aligns with your needs.
Reviewing Policy Details
Thorough review of policy details is paramount before making a purchase. Understanding the terms and conditions of the policy is critical to avoid any unforeseen complications or surprises later. Carefully examine the coverage limits, exclusions, and any specific requirements. Read the fine print, including clauses related to pre-existing conditions, waiting periods, and limitations on coverage. Seeking clarification from the insurance provider regarding any unclear aspects is essential.
Understanding all details helps to make informed decisions and prevent potential future issues.
Steps to Choosing an Insurance Plan
| Step | Action |
|---|---|
| 1 | Identify your needs and budget. |
| 2 | Research different health insurance plans and life insurance policies. |
| 3 | Compare plans based on coverage, costs, and provider networks. |
| 4 | Request detailed policy information and ask clarifying questions. |
| 5 | Compare and contrast different insurance providers’ financial strength and reputation. |
| 6 | Carefully review policy terms and conditions. |
| 7 | Seek expert advice or a financial advisor if needed. |
| 8 | Make a well-informed decision based on your specific requirements. |
Illustrative Examples
Understanding the nuances between health and life insurance requires examining real-world scenarios. These examples highlight how each type of coverage addresses distinct needs and financial uncertainties. Different life events necessitate different types of protection, and the right coverage can make a significant difference in navigating challenging times.
Real-World Scenarios Where Health Insurance Is Essential
Health insurance plays a crucial role in managing unexpected medical expenses. Without it, a seemingly minor injury or illness can quickly become a significant financial burden. Here are some illustrative scenarios:
- A young professional suffers a severe injury in a workplace accident requiring extensive surgery and rehabilitation. High medical costs could quickly deplete their savings and lead to significant financial stress without health insurance.
- A family faces a sudden illness requiring prolonged hospital stays and specialized treatments for a child. The associated costs can quickly spiral out of control, potentially overwhelming their budget without health insurance.
- An elderly individual experiences a serious health complication, such as a stroke or heart attack, requiring long-term care and potentially expensive medications. Health insurance is critical to manage these expenses.
- A pregnant woman experiences complications during pregnancy leading to a premature birth. The associated medical costs, including neonatal intensive care, can be substantial and potentially crippling without health insurance coverage.
Real-World Scenarios Where Life Insurance Is Essential
Life insurance safeguards loved ones’ financial future when a primary income earner passes away. It helps ensure that dependents are not left financially vulnerable. The following examples illustrate the significance of life insurance:
- A young couple with a newborn child has a limited financial cushion. Life insurance ensures the child’s future is financially secure in case of the parent’s untimely death.
- A single parent working to provide for their children relies on life insurance to secure their children’s education, future needs, and provide financial stability.
- A business owner with a significant investment in their business needs life insurance to provide funds for their business continuity in case of death.
- An individual with outstanding debts, such as a mortgage or student loans, requires life insurance to settle these obligations and protect their family from financial hardship.
Difference Between Health and Life Insurance in the Event of an Accident
Health insurance covers the medical expenses arising from an accident. It addresses the
- treatment* of the injury. Life insurance, on the other hand, provides a financial payout to beneficiaries in case of death due to the accident. It addresses the
- financial implications* of the loss of life.
Difference Between Health and Life Insurance in the Event of a Terminal Illness
Health insurance covers the costs of treatment for a terminal illness. It addresses the
- medical expenses* associated with the illness. Life insurance, however, is not directly involved in the treatment costs, but it provides a financial safety net for beneficiaries in the event of death. It addresses the
- financial impact* of the illness on loved ones.
Scenario Highlighting the Need for Both Types of Insurance
A young professional, recently married and expecting a child, has a substantial mortgage and plans for their child’s future. A sudden illness, requiring lengthy hospitalization and extensive medical treatments, could quickly deplete their savings. Health insurance is vital to cover these expenses. Should the young professional pass away during this period, life insurance would ensure the financial security of their spouse and newborn child, covering the mortgage, child’s education, and other expenses.
This highlights the importance of having both health and life insurance for comprehensive financial protection.
Claims Process: Health Vs Life Insurance: Key Differences
Navigating the claims process for both health and life insurance can be intricate. Understanding the steps involved and potential roadblocks can ease the process and ensure a smoother outcome. This section details the typical procedures for filing and processing claims, highlighting key differences between the two types of insurance and common reasons for denials. Thorough record-keeping is crucial to a successful claim.
Health Insurance Claim Process
The health insurance claims process typically involves several steps. First, you need to gather all necessary documentation, including the claim form, medical bills, receipts, and any pre-authorization or referral information required by the insurance company. Next, submit the completed claim form and supporting documents to the insurance company via the designated method, such as mail, online portal, or fax.
The insurance company will then review the claim, potentially requesting further information or clarification. Once approved, the insurance company will process the payment according to the terms of your policy. If the claim is denied, you will receive a written explanation outlining the reasons for the denial, and you may have the opportunity to appeal the decision.
Life Insurance Claim Process
The life insurance claim process usually involves providing documentation to support the death certificate, policy details, and other relevant information to the insurance company. This typically includes the death certificate, proof of identity of the claimant, and a copy of the life insurance policy. The insurance company will investigate the claim, verify the death, and assess the validity of the claim.
Once approved, the insurance company will pay the death benefit to the designated beneficiary(ies) according to the policy terms. If the claim is denied, you will receive a formal explanation outlining the reasons for the denial, and you may have the opportunity to appeal the decision.
Common Reasons for Claim Denials
Claim denials, whether for health or life insurance, often stem from a failure to meet policy requirements or procedural errors. For health insurance, this could include a lack of pre-authorization, incorrect or incomplete documentation, or the treatment not being considered medically necessary by the insurance company. In life insurance, denials can occur due to misrepresentation of facts, failure to meet policy conditions, or lack of proper documentation.
Importance of Accurate Records
Maintaining accurate records is paramount to a successful claim. Thorough documentation, including receipts, medical bills, and policy information, is critical for supporting the claim and reducing the likelihood of delays or denials. This also aids in the claims review and processing stages. Accurate records ensure all required information is readily available, leading to a smoother and more efficient claims process.
Structured Claims Process
| Insurance Type | Claim Filing Steps |
|---|---|
| Health Insurance |
|
| Life Insurance |
|
Final Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Health vs Life Insurance: Key Differences highlights the critical distinctions between these essential insurance types. Choosing the right coverage depends heavily on individual circumstances and financial goals. This guide has provided a detailed comparison of their respective features, benefits, and costs. By understanding the unique characteristics of each, you can make informed decisions about your insurance needs and ensure comprehensive protection for yourself and your loved ones.
Popular Questions
What are the common exclusions in a health insurance plan?
Common exclusions vary by plan but often include pre-existing conditions (depending on the plan), cosmetic procedures, and certain alternative therapies.
How are life insurance premiums calculated?
Life insurance premiums are calculated based on factors such as your age, health, lifestyle, and the desired coverage amount.
What are some situations where both health and life insurance are crucial?
Situations where both are important include those involving chronic illnesses, significant long-term care needs, and families with dependent children.
What are the steps in purchasing a life insurance policy?
Steps generally include application, medical evaluation, policy selection, premium payment, and review of policy details.





