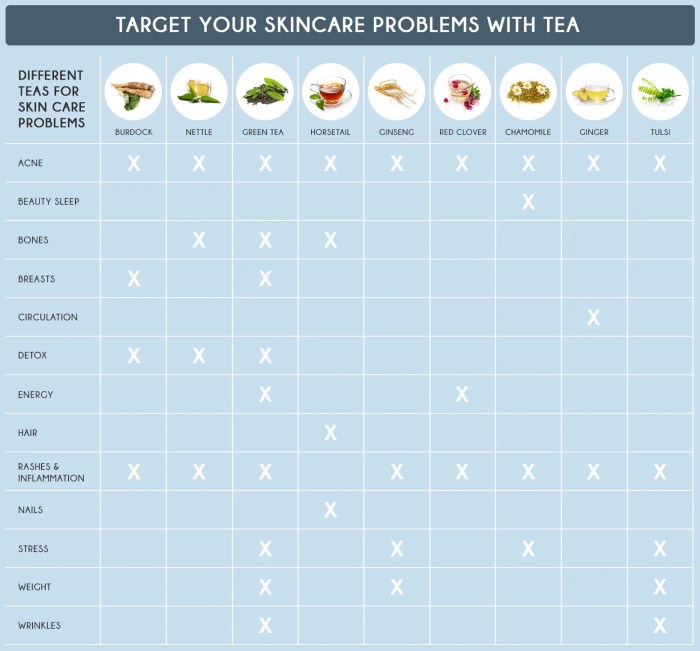
Coffee And Tea Weight Loss Allies
Coffee and Tea: Weight Loss Allies explores the fascinating ways these beverages can support weight management. From their impact on metabolism and appetite regulation to their role in hydration, this comprehensive guide examines the potential benefits and considerations surrounding coffee and tea consumption for weight loss.
This analysis delves into the intricate relationship between these popular drinks and weight loss, considering various factors such as brewing methods, individual responses, and potential interactions with medications. We’ll explore the science behind their effects on metabolic rate, appetite, and hydration, while also acknowledging the importance of a balanced lifestyle approach.
Coffee and Tea’s Impact on Metabolism
Coffee and tea, enjoyed globally, are often associated with potential metabolic benefits. Understanding their impact on the body’s metabolic processes requires examining the effects of caffeine, antioxidants, and preparation methods. This exploration delves into the complex relationship between these beverages and metabolic rate, highlighting key considerations for those interested in their potential role in weight management.Caffeine, a stimulant found in both coffee and tea, is a key player in influencing metabolic rate.
It acts by stimulating the central nervous system, increasing heart rate and oxygen consumption. This heightened activity can lead to a temporary increase in energy expenditure, potentially contributing to a slight boost in metabolic rate. However, the effect is typically modest and varies considerably between individuals.
Caffeine’s Influence on Metabolic Rate
Caffeine’s impact on metabolic rate is multifaceted, with several mechanisms at play. It primarily affects the body’s thermogenesis, the process of generating heat to maintain body temperature. Increased thermogenesis leads to an elevated energy expenditure, which can contribute to a slight increase in metabolic rate. Furthermore, caffeine can stimulate the breakdown of fat stores, albeit to a limited extent.
The precise magnitude of this effect remains an area of ongoing research, with varying results depending on factors like individual metabolism, body composition, and the amount of caffeine consumed.
Comparison of Coffee and Tea’s Impact
The metabolic impact of coffee and tea can differ depending on factors such as brewing method and preparation. Generally, brewed coffee tends to have a higher caffeine content compared to tea, leading to a potentially more pronounced metabolic effect. However, the specific effects can vary based on the type of tea (e.g., black tea, green tea, oolong tea), as well as the brewing method used for both coffee and tea.
The presence of other compounds in tea, like polyphenols, can contribute to a broader range of potential health benefits beyond the effects of caffeine.
Role of Antioxidants in Metabolic Processes
Coffee and tea are rich sources of antioxidants, particularly polyphenols. These compounds play a crucial role in protecting cells from damage caused by free radicals. The presence of antioxidants in these beverages may contribute to overall health and potentially influence metabolic processes. However, the exact nature and extent of these interactions remain a subject of active research.
A diet rich in antioxidant-rich foods like coffee and tea may be associated with improved metabolic health, but more research is needed to confirm these potential links.
Caffeine Content in Various Beverages
The following table provides a general comparison of caffeine content in various coffee and tea types. Note that these values can vary based on factors such as bean variety, brewing method, and preparation type.
| Beverage Type | Approximate Caffeine Content (mg) |
|---|---|
| Brewed Coffee (8 oz) | 90-160 |
| Espresso (1 oz) | 60-80 |
| Black Tea (8 oz) | 40-60 |
| Green Tea (8 oz) | 20-40 |
| Herbal Tea (8 oz) | 0 |
Impact of Added Milk and Sweeteners
The addition of milk or sweeteners to coffee and tea can affect their metabolic impact. Milk, particularly whole milk, can increase the caloric content of the beverage. Sweeteners, such as sugar, also add calories and may have potential negative impacts on blood sugar regulation, potentially affecting metabolic processes. The choice of milk type and sweetener significantly impacts the overall nutritional profile and calorie count.
For example, using low-fat milk or alternatives like almond milk can reduce the caloric load. Similarly, using natural sweeteners in moderation can be a consideration.
Effect on Appetite and Calorie Intake: Coffee And Tea: Weight Loss Allies
Coffee and tea, enjoyed globally, are often associated with potential weight management benefits. Beyond their metabolic effects, these beverages can influence appetite and calorie intake, playing a role in weight loss strategies. This section explores the nuanced relationship between coffee and tea consumption and feelings of fullness, examining the impact on calorie intake across various individuals.While the effects of coffee and tea on appetite can vary, research suggests that both beverages can contribute to feelings of satiety and potentially reduce overall calorie intake.
This effect is multifaceted and influenced by individual factors such as metabolism, overall diet, and specific preparation methods.
Impact on Feelings of Fullness and Satiety
Coffee and tea, thanks to their bioactive compounds, including caffeine and various antioxidants, can impact the digestive system. Caffeine, in particular, has been linked to increased thermogenesis and reduced appetite in some individuals. This can lead to a sense of fullness, potentially reducing the urge to overeat. However, the extent to which these effects occur varies greatly between people.
Some individuals might experience a noticeable reduction in appetite, while others may not. This individual variation is crucial to understanding the complex interplay between coffee/tea consumption and appetite regulation.
Comparison of Appetite Suppression in Different Individuals
The impact of coffee and tea on appetite suppression is not uniform. Factors such as individual metabolism, genetics, existing dietary habits, and overall health conditions can significantly influence how a person responds to these beverages. For example, individuals with higher metabolic rates may experience a more pronounced appetite-suppressing effect from coffee or tea compared to those with lower metabolic rates.
Similarly, individuals with pre-existing conditions like eating disorders may need to be cautious in increasing coffee/tea consumption, as it might exacerbate specific sensitivities.
Studies on Coffee/Tea Consumption and Calorie Intake
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between coffee and tea consumption and calorie intake. Some studies have shown a correlation between regular coffee consumption and a slight decrease in daily calorie intake, although the magnitude of this effect can vary. Similarly, research on tea consumption has shown similar trends, with potential benefits observed in some cases. However, it’s important to remember that these are often observational studies, and causality cannot be definitively established.
The exact mechanisms by which coffee and tea influence calorie intake are still under active investigation.
Table of Coffee/Tea Preparation Methods and Potential Impact on Appetite
| Preparation Method | Potential Impact on Appetite | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Brewed Coffee (regular) | Moderate | Moderate effect on appetite suppression, potentially due to caffeine content. |
| Espresso | High | Higher caffeine concentration, potentially leading to more pronounced appetite suppression. |
| Decaf Coffee | Low | Absence of caffeine may result in a minimal effect on appetite. |
| Herbal Tea (e.g., chamomile) | Low to Moderate | No caffeine, but some herbal teas may have mild effects on appetite through other compounds. |
| Black Tea | Moderate | Contains caffeine, potentially contributing to appetite suppression. |
| Green Tea | Moderate | Contains caffeine and other antioxidants, which may influence appetite and metabolism. |
Incorporating Coffee and Tea into a Balanced Weight Loss Diet
A balanced weight loss diet should encompass a variety of nutrient-rich foods and appropriate portions. Coffee and tea can be seamlessly incorporated into such a plan. Consider these suggestions:
- Moderate Consumption: Limit coffee and tea intake to avoid potential negative side effects, such as anxiety or sleep disturbances, especially for individuals sensitive to caffeine.
- Hydration: Both coffee and tea, when consumed in moderation, can contribute to overall hydration, which is essential for various bodily functions.
- Mindful Consumption: Enjoy coffee and tea mindfully, paying attention to how they affect your appetite and overall well-being. This approach allows for a personalized understanding of your body’s response to these beverages.
- Balanced Meal Plan: Ensure a well-balanced diet alongside coffee and tea consumption. Focus on consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
Hydration and its Role in Weight Management

Proper hydration is crucial for overall health and plays a significant role in weight management. Water is essential for numerous bodily functions, including nutrient transport, waste elimination, and temperature regulation. Maintaining adequate hydration can contribute to a feeling of fullness, reducing the likelihood of overeating and supporting healthy weight maintenance.Staying adequately hydrated is a key element in a comprehensive weight management strategy.
This is because proper hydration aids in the metabolic processes vital for burning calories. Furthermore, the feeling of satiety often associated with sufficient hydration can help individuals manage their calorie intake effectively.
Importance of Hydration for Overall Health
Adequate hydration is essential for various physiological processes. It supports nutrient absorption, assists in the removal of waste products, and plays a crucial role in maintaining body temperature. Proper hydration also lubricates joints and protects tissues, contributing to overall well-being. The human body is composed of approximately 60% water, highlighting the vital role hydration plays in maintaining bodily functions.
How Coffee and Tea Contribute to Daily Fluid Intake
Both coffee and tea, when consumed in moderation, can contribute significantly to daily fluid intake. While the caffeine content in these beverages may have diuretic effects, a balanced intake, along with sufficient water consumption, can still support overall hydration. Many individuals incorporate coffee and tea into their daily routine, making them valuable components of a hydration strategy.
Health Benefits of Staying Hydrated
- Improved Metabolism: Hydration facilitates metabolic processes, potentially leading to enhanced calorie burning. Adequate hydration helps the body function optimally, including metabolic processes.
- Enhanced Physical Performance: Water is crucial for muscle function and performance. Sufficient hydration can improve endurance and energy levels, supporting physical activities conducive to weight management.
- Reduced Appetite: Sometimes, feelings of hunger can be mistaken for thirst. Drinking water before meals can help reduce the perception of hunger, potentially leading to lower calorie intake.
- Improved Nutrient Absorption: Water is essential for transporting nutrients throughout the body, ensuring that the body effectively utilizes the nutrients from food.
- Better Skin Health: Hydration plays a vital role in maintaining skin elasticity and preventing dryness. This contributes to a healthy and youthful appearance.
- Proper Waste Removal: Water helps the body eliminate waste products efficiently. Adequate hydration supports the excretory system, facilitating the removal of toxins and byproducts.
Potential Negative Effects of Excessive Coffee and Tea Consumption on Hydration, Coffee and Tea: Weight Loss Allies
Excessive consumption of coffee and tea, particularly those with high caffeine content, can lead to dehydration if not balanced with sufficient water intake. The diuretic effect of caffeine can increase the rate of fluid loss from the body, potentially counteracting the hydration benefits of these beverages.
Comparison of Hydration Properties of Various Coffee and Tea Types
| Beverage Type | Caffeine Content (mg/cup) | Antioxidant Properties | Diuretic Potential | Potential Hydration Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brewed Coffee (Dark Roast) | 100-200 | Moderate | High | Moderate, if consumed with sufficient water |
| Brewed Coffee (Light Roast) | 75-150 | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate, if consumed with sufficient water |
| Black Tea | 20-50 | High | Moderate | Moderate, if consumed with sufficient water |
| Green Tea | 20-40 | High | Moderate | Moderate, if consumed with sufficient water |
| Herbal Tea (e.g., Peppermint) | 0 | Variable | Low | High, excellent alternative |
Note: Caffeine content and antioxidant properties may vary based on brewing methods and preparation. The table provides a general overview.
Potential Interactions with Medications
While coffee and tea offer numerous health benefits, including potential weight management support, it’s crucial to understand their potential interactions with various medications. These interactions can significantly impact the effectiveness and safety of certain treatments. Awareness of these potential risks is essential for responsible consumption.Understanding how coffee and tea can affect medication absorption, metabolism, and overall physiological response is paramount.
The concentration of active ingredients in these beverages, as well as the brewing method used, can influence their interaction with medication. This information empowers individuals to make informed choices about their consumption habits, especially if they are taking prescribed medications.
Potential Drug Interactions
Various medications can experience altered absorption, metabolism, or overall physiological effects when consumed alongside coffee or tea. The caffeine and other bioactive compounds in these beverages can interfere with the way certain drugs are processed by the body.
Impact of Brewing Methods
The brewing method used can significantly impact the amount of active compounds, such as caffeine, present in the final product. For instance, drip coffee makers typically extract more caffeine compared to French press methods. Similarly, different tea brewing techniques can yield varying levels of bioactive compounds, impacting the potential for drug interactions. The length of steeping time for tea, and the water temperature used during brewing, also influence the final concentration of active compounds.
List of Medications Known to Interact with Coffee or Tea
Several medications are known to have potential interactions with coffee and tea, including but not limited to:
- Anticoagulants (blood thinners): These medications can have their effectiveness altered by caffeine, leading to either increased or decreased blood thinning effects. This variation can increase the risk of bleeding or clotting, depending on the specific interaction.
- Antidepressants and mood stabilizers: Caffeine can potentially affect the efficacy of these medications. The combined effects might intensify or diminish the therapeutic benefits, and could also cause unwanted side effects.
- Antihistamines: Caffeine can potentially exacerbate the sedative effects of some antihistamines, increasing drowsiness and other side effects.
- Certain antibiotics and medications for gastrointestinal issues: The presence of caffeine in coffee and tea can influence the absorption of certain medications, potentially diminishing their efficacy or causing discomfort.
Potential Drug Interaction Table
The table below illustrates potential interactions between specific medications and coffee/tea consumption, categorized by the type of medication. It is crucial to remember that this is not an exhaustive list and individual responses can vary. Consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
| Medication Type | Coffee/Tea Consumption | Potential Interaction |
|---|---|---|
| Anticoagulants | High caffeine intake | Increased risk of bleeding or clotting |
| Antidepressants | High caffeine intake | Potentially diminished or intensified therapeutic effects |
| Antihistamines | Combined consumption | Increased drowsiness and other side effects |
| Certain Antibiotics | Simultaneous intake | Potential alteration of absorption, reduced effectiveness |
| Gastrointestinal Medications | Coffee/Tea Consumption | Potential interference with absorption, discomfort |
Other Factors to Consider
While coffee and tea consumption can contribute positively to weight management by influencing metabolism, appetite, and hydration, it’s crucial to acknowledge that individual responses and lifestyle factors play a significant role. Understanding these nuances can help tailor a personalized approach to weight management that incorporates these beverages effectively.Individual differences in how people respond to coffee and tea are considerable.
Genetic predispositions, existing health conditions, and overall dietary habits all contribute to the varied impact these beverages have on metabolism, appetite regulation, and weight. For instance, some individuals might experience a heightened metabolic boost from coffee, while others might find it has little effect. Similarly, the effect on appetite suppression can vary significantly from person to person.
Individual Variations in Response
Individual differences in physiology, genetics, and existing health conditions significantly impact how individuals respond to coffee and tea consumption. This variability necessitates a personalized approach to incorporating these beverages into weight management strategies.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors like exercise, sleep, and stress levels significantly influence the effectiveness of coffee and tea in weight management. A balanced approach that incorporates regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management techniques is crucial for maximizing the potential benefits of these beverages. Consistent exercise, combined with moderate coffee intake, can lead to improved calorie expenditure. Sufficient sleep, often overlooked, is vital for regulating hormones and appetite, and a lack of it can lead to increased cravings and impaired metabolism, which can negate the positive effects of coffee or tea.
Coffee and Tea Preparation Methods
The method of preparation can influence the perceived effects of coffee and tea. For instance, brewing methods like French press or cold brew can yield different levels of caffeine and other compounds, affecting metabolic rate and perceived stimulation. The level of processing of the coffee beans, such as roasting, can also affect the chemical composition and influence the impact on the body.
Additionally, the type of milk or sugar added to coffee or tea can affect the calorie and sugar content, potentially impacting weight management goals.
Alternative Beverages
Several alternative beverages offer similar properties to coffee and tea without the caffeine or specific compounds that might be problematic for certain individuals. Herbal infusions, green tea alternatives, or naturally decaffeinated coffee substitutes can offer comparable benefits, such as hydration and potential metabolic effects, while minimizing the potential side effects of caffeine.
Nutritional Profiles of Coffee and Tea Varieties
| Beverage | Caffeine (mg) | Antioxidants (mg) | Calories (kcal) | Sugar (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Decaf Coffee (8oz) | 0-2 | Variable | 2-4 | 0-0.5 |
| Regular Coffee (8oz) | 95-165 | Variable | 2-4 | 0-0.5 |
| Black Tea (8oz) | 20-50 | Variable | 2-4 | 0-0.5 |
| Green Tea (8oz) | 20-50 | High | 2-4 | 0-0.5 |
Note: Nutritional values can vary significantly depending on the specific origin, preparation method, and brand. This table provides a general overview. Always check the specific product label for detailed information.
Addressing Common Misconceptions
Coffee and tea, while often associated with weight loss, are not a magic bullet. Understanding the nuances of their impact is crucial to avoiding unrealistic expectations and potential pitfalls. Misconceptions about their effects can lead to frustration and potentially harmful habits. This section clarifies common misinterpretations surrounding these beverages’ role in weight management.Many people mistakenly believe that coffee and tea directly lead to significant weight loss.
While they can influence metabolism and appetite, these effects are not always substantial enough to cause dramatic changes on their own. Furthermore, an unbalanced diet and lack of exercise will often negate the benefits of these beverages. The focus should always be on a holistic approach to weight management.
Common Misconceptions about Weight Loss
Several common misconceptions surround the impact of coffee and tea on weight loss. People may believe that these beverages burn significant calories or suppress appetite in ways that are not supported by scientific evidence. Some believe that the perceived increase in energy expenditure associated with these beverages directly translates to significant weight loss, which is not always the case.
Reasons for Perceived Weight Gain
Some individuals perceive coffee and tea as contributing to weight gain, often due to accompanying dietary choices. For instance, if someone frequently consumes high-calorie beverages like sweetened coffee or tea lattes, the additional calories from sugar or cream can outweigh any potential metabolic benefits. Similarly, if an individual replaces healthy meals with frequent coffee or tea breaks, this can lead to an overall calorie surplus.
Negative Impacts of Excessive Consumption
Excessive coffee and tea consumption can lead to several negative consequences. These include anxiety, sleep disturbances, and digestive issues. It’s important to listen to your body and adjust consumption to maintain a healthy balance.
Negative Impacts on Sleep
Caffeine, present in both coffee and tea, can interfere with sleep quality. Consuming these beverages too close to bedtime can lead to difficulty falling asleep or maintaining sleep. The effects of caffeine can vary depending on individual sensitivity. It’s important to consider individual tolerances when scheduling caffeine intake.
- Reduced sleep duration: Excessive caffeine intake can lead to shorter sleep duration, impacting overall rest and recovery.
- Sleep disturbances: The stimulating effect of caffeine can lead to interrupted sleep, making it difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep.
- Insomnia: In some individuals, excessive caffeine consumption can contribute to insomnia, characterized by difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep.
Decaf vs. Caffeinated Coffee and Tea
Decaf coffee and tea, while lacking the stimulating effects of their caffeinated counterparts, can still provide similar benefits related to hydration and potential antioxidants. The absence of caffeine can make them a suitable alternative for those sensitive to caffeine’s effects or those looking to avoid sleep disturbances.
| Characteristic | Caffeinated | Decaffeinated |
|---|---|---|
| Stimulating effect | High | Low |
| Potential sleep disruption | Higher | Lower |
| Antioxidant content | Potentially similar | Potentially similar |
| Hydration | Good | Good |
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, Coffee and Tea: Weight Loss Allies highlights the potential of these beverages to support weight management strategies. However, individual responses vary, and a balanced approach incorporating a healthy diet, regular exercise, and sufficient sleep is crucial. Understanding the potential interactions with medications and addressing common misconceptions are key to making informed choices. By thoughtfully considering the factors discussed in this guide, you can better harness the potential of coffee and tea for a healthier lifestyle.
Popular Questions
What is the recommended daily intake of coffee or tea for weight management?
There’s no single recommended daily intake. Individual needs vary based on factors like metabolism, tolerance, and overall dietary habits. Moderation is key. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Can decaffeinated coffee or tea offer similar benefits to their caffeinated counterparts regarding weight loss?
While decaffeinated options retain some antioxidants and may contribute to hydration, their impact on metabolism and appetite might be slightly less pronounced compared to caffeinated varieties. Individual responses vary.
How do different brewing methods affect the caffeine content and potential impact on weight loss?
Different brewing methods (e.g., drip, French press, pour-over) can influence caffeine extraction. Stronger brews generally contain more caffeine. However, the overall impact on weight loss is often influenced by individual factors beyond brewing techniques.
Are there any specific types of milk or sweeteners that are particularly beneficial or detrimental to weight loss when consumed with coffee or tea?
Some milk options (e.g., unsweetened almond milk) are lower in calories than others. Excessive added sugar from sweeteners can counteract weight loss efforts. Moderation is key for all additions.