Auto Loan Rates 2025
Auto Loan Rates 2025: Market Trends explores the anticipated trajectory of auto loan rates throughout the year. This in-depth analysis delves into the various factors influencing these rates, from economic indicators to consumer behavior, providing a comprehensive understanding of the market dynamics.
The report examines the potential impact of inflation, interest rates, and GDP growth on loan costs. It also contrasts rates for different vehicle types, considering factors such as new versus used cars, and electric versus traditional models. The analysis further investigates how government policies and consumer preferences might shape loan demand and availability.
Overview of Auto Loan Rates in 2025
Auto loan rates in 2025 are anticipated to be influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors. While a precise prediction is impossible, several trends suggest potential paths. The trajectory of interest rates, inflation, and economic growth will be key determinants. Historical data and current economic conditions provide some insight into potential outcomes.Economic conditions, including employment levels and consumer confidence, are pivotal in shaping demand and the overall lending environment.
Inflationary pressures, particularly if persistent, can increase borrowing costs. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions will also have a substantial impact on the cost of borrowing for auto loans. A careful assessment of these factors is necessary to understand the likely range of auto loan rates in 2025.
Projected Trends in Auto Loan Rates for 2025
A variety of factors will contribute to the anticipated range of auto loan rates in 2025. These factors include persistent inflation, the potential for a softening or cooling economy, and adjustments in the Federal Reserve’s interest rate policies.
Key Economic Indicators Affecting Auto Loan Rates
Understanding the likely trajectory of key economic indicators will provide valuable insight into potential auto loan rate fluctuations.
| Indicator | Description | Expected Trend | Impact on Rates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inflation Rate | The rate at which the general level of prices for goods and services is rising. | Potentially moderate, but with some lingering upward pressure. | Higher inflation typically leads to higher interest rates, potentially increasing auto loan rates. |
| Gross Domestic Product (GDP) Growth | The monetary value of all finished goods and services produced within a country’s borders in a specific time period. | Likely to slow from 2024 levels. | Slower GDP growth might lead to a less robust economy, potentially affecting consumer demand and consequently, auto loan rates. |
| Unemployment Rate | The percentage of the labor force that is actively looking for work but unable to find employment. | Potentially stable or slightly increasing. | A higher unemployment rate could weaken consumer confidence and potentially reduce demand for auto loans, which may put downward pressure on rates. |
| Federal Funds Rate | The target rate set by the Federal Reserve at which commercial banks lend money to each other overnight. | Likely to remain relatively high or increase slightly, depending on inflation trends. | Changes in the Federal Funds Rate are often directly correlated with changes in auto loan rates. |
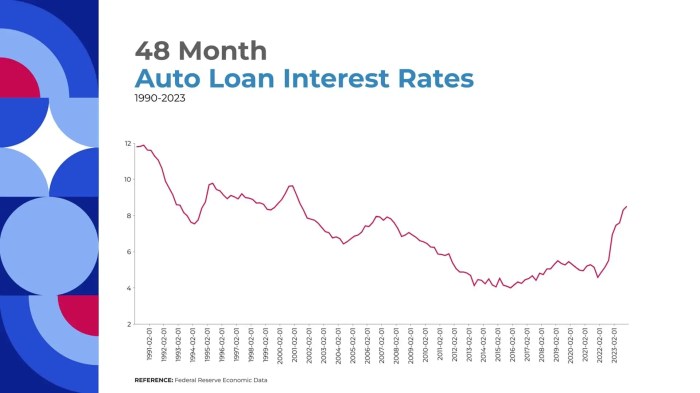
Visual Representation of Projected Auto Loan Rates
Graph depicting anticipated auto loan rates, highlighting possible fluctuations.
Note: The graph would visually illustrate the projected range of auto loan rates in 2025, showing potential highs and lows. It would be dynamic, illustrating the effect of the various economic factors on the overall trend. The precise shape of the graph would depend on the actual outcomes of the economic indicators.
Comparison of Auto Loan Rates Across Different Sectors
Auto loan rates in 2025 are expected to exhibit variations across different vehicle types and sectors. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for consumers seeking financing and for financial institutions evaluating risk and return. Factors such as vehicle age, type, and market demand will significantly influence the interest rates offered.The divergence in auto loan rates across various sectors stems from the differing levels of risk associated with each vehicle type.
This assessment takes into account factors like anticipated depreciation, potential for damage, and the overall demand for the specific type of vehicle. These considerations ultimately affect the interest rates charged by lending institutions.
Comparison of New and Used Vehicle Loan Rates
The projected auto loan rates for new vehicles will likely be lower than those for used vehicles. This difference arises from the lower risk associated with new vehicles, which typically have a higher residual value and lower anticipated depreciation. Lenders perceive new vehicles as having a reduced chance of substantial damage or mechanical issues, translating into a lower perceived risk and a correspondingly lower interest rate.
Used vehicles, on the other hand, present a higher risk due to factors such as pre-existing damage or potential wear and tear, which may necessitate repairs and affect the vehicle’s resale value.
Comparison of Electric and Traditional Vehicle Loan Rates
Electric vehicles (EVs) are expected to see competitive loan rates in 2025. This favorable position reflects a combination of factors, including government incentives, and the increased demand for EVs, which may lead to higher residual values. This creates a lower perceived risk for lenders. Conversely, traditional gasoline-powered vehicles may see slightly higher loan rates due to the established market and the relatively slower adoption of electric vehicles.
However, this trend may shift as the EV market matures.
Projected Auto Loan Rates for 2025
| Vehicle Type | Loan Term (Years) | Interest Rate (Estimated Range) | Factors Influencing Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| New Electric Vehicle | 5 | 3.5% – 5.5% | Government incentives, high demand, lower projected depreciation |
| Used Electric Vehicle | 5 | 4.5% – 6.5% | Lower demand, variable residual value, age and mileage |
| New Traditional Vehicle | 5 | 4.0% – 6.0% | Established market, varying levels of demand, expected depreciation |
| Used Traditional Vehicle | 5 | 5.0% – 7.5% | Age and mileage, higher risk of repairs, depreciation |
Financial Institution Lending Policies
Financial institutions are expected to tailor their lending policies to cater to the distinct characteristics of different vehicle types. For instance, banks and credit unions may offer more favorable rates for new and electric vehicles due to the lower perceived risk. This differentiation could manifest in the form of reduced loan amounts, different loan terms, or specific programs designed to encourage consumers to purchase these vehicles.
Conversely, they may adjust lending policies for used vehicles to mitigate the higher risk associated with potential repairs and lower residual values. Credit scores and the borrower’s overall financial health will continue to play a critical role in loan approval and interest rates.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Auto Loan Rates
The economic climate significantly influences auto loan rates. Factors like GDP growth, unemployment figures, and inflation all play crucial roles in shaping the cost of borrowing for car purchases. Understanding these relationships is essential for both consumers and lenders in anticipating future trends.Economic indicators provide a valuable window into the overall health of the market. These indicators can signal whether the economy is expanding or contracting, and this directly affects the risk profile for lenders.
In a robust economy, borrowers are typically more creditworthy, allowing lenders to offer more favorable loan terms. Conversely, during periods of economic downturn, the risk of default increases, which often leads to higher interest rates to compensate for the added risk. The interplay between these factors is critical to predicting future auto loan rates.
GDP Growth and Unemployment Rates
GDP growth and unemployment rates are key economic indicators that provide insight into the overall health of the economy. Strong GDP growth, coupled with low unemployment rates, usually points to a robust job market and increased consumer spending power. This environment typically translates to a lower risk of default for borrowers, allowing lenders to offer more competitive interest rates on auto loans.
Conversely, periods of economic slowdown or high unemployment rates raise the risk of default, potentially leading to higher auto loan interest rates. For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, high unemployment and slow GDP growth resulted in significantly higher auto loan rates as lenders adjusted their risk assessments.
Inflation and Auto Loan Rates
Inflation’s impact on auto loan rates is often indirect but substantial. High inflation erodes the purchasing power of money, increasing the real cost of borrowing for consumers. Lenders, in response to this erosion, may raise interest rates to maintain their profit margins, which in turn raises the cost of auto loans. This dynamic is often complex and influenced by other economic factors, but the relationship is undeniable.
Historically, periods of high inflation have coincided with increases in auto loan rates.
Interest Rate Adjustments and Auto Loan Costs
Central bank interest rate adjustments directly impact the cost of borrowing for auto loans. When central banks raise interest rates, the cost of borrowing for all types of loans, including auto loans, increases. This is because the benchmark interest rates set by central banks influence the interest rates offered by lending institutions. Conversely, when central banks lower interest rates, the cost of borrowing for auto loans tends to decrease.
This adjustment reflects the broader financial environment and the associated risk assessments of lenders. For instance, the Federal Reserve’s rate adjustments in recent years have had a demonstrable effect on auto loan interest rates.
Relationship Between Economic Indicators and Auto Loan Rates
| Economic Indicator | Description | Expected Impact | Potential Rate Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth | The rate at which a country’s economy expands. | Stronger growth usually indicates a healthier economy, lowering the risk of default. | Potential for lower auto loan rates. |
| Unemployment Rate | The percentage of the labor force that is unemployed. | Lower unemployment generally signifies a stronger labor market and increased consumer spending. | Potential for lower auto loan rates. |
| Inflation Rate | The rate at which prices for goods and services increase over time. | High inflation reduces the purchasing power of money and increases the cost of borrowing for consumers. | Potential for higher auto loan rates. |
| Interest Rate Adjustments | Changes in benchmark interest rates set by central banks. | These adjustments directly affect the cost of borrowing for auto loans. | Potential for higher or lower rates depending on the direction of the adjustment. |
Consumer Behavior and Loan Demand in 2025: Auto Loan Rates 2025
Consumer behavior is a key driver in the auto loan market, directly impacting both demand and supply. Understanding anticipated trends in consumer spending, confidence, and preferences is crucial for forecasting auto loan rates and market dynamics in 2025. Factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and the emergence of new technologies like electric vehicles will all shape how consumers approach purchasing a car.Anticipated consumer behavior regarding auto purchases in 2025 will be influenced by a confluence of factors.
Consumer confidence levels, economic growth projections, and prevailing interest rates will all play a significant role in shaping the demand for auto loans. A robust economy with low unemployment, coupled with favorable interest rates, is likely to boost consumer confidence and encourage auto purchases, thus driving loan demand. Conversely, an economic downturn or high-interest rates could lead to a decline in auto loan demand.
Consumer Confidence and Spending Patterns
Consumer confidence directly correlates with the willingness to take on debt for large purchases like automobiles. Historical data demonstrates a strong positive correlation between consumer confidence and auto loan demand. Periods of economic uncertainty often lead to decreased consumer confidence and, consequently, a reduced demand for auto loans. For instance, during the 2008 financial crisis, consumer confidence plummeted, causing a significant drop in auto loan applications.
Conversely, periods of strong economic growth, coupled with low unemployment rates, tend to foster higher consumer confidence and increased auto loan demand. Current economic forecasts and projections of future economic conditions are crucial for understanding consumer confidence levels in 2025 and their subsequent impact on auto loan demand.
Impact of Consumer Borrowing Habits, Auto Loan Rates 2025
Consumer borrowing habits, including credit scores, debt-to-income ratios, and repayment history, are critical factors in assessing the ability of consumers to secure auto loans. Lenders carefully evaluate these factors to assess risk and determine appropriate interest rates. Consumers with strong credit histories and low debt-to-income ratios are more likely to qualify for favorable loan terms, while those with weaker credit profiles may face higher interest rates or difficulty securing financing.
Changes in consumer borrowing habits, such as an increase in the use of alternative financing options, could affect the supply and demand dynamics in the auto loan market.
Impact of Changing Consumer Preferences
Changing consumer preferences, particularly the increasing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), will profoundly impact the demand for auto loans. The evolving market for EVs presents both opportunities and challenges for lenders. The rising popularity of EVs could lead to increased demand for loans for purchasing these vehicles, creating new opportunities for lenders in a rapidly expanding market segment.
However, unique factors surrounding EVs, such as the potential for higher upfront costs and varying charging infrastructure, may also affect the demand for traditional auto loans. Moreover, the evolving regulatory landscape and incentives for EV adoption could further shape consumer preferences and loan demand in 2025. For example, government subsidies for EV purchases could incentivize consumers to opt for EVs, potentially leading to a decrease in demand for conventional vehicles and impacting loan demand in the conventional auto loan sector.
Loan Terms and Their Impact on Rates
Loan terms significantly influence the cost of borrowing for an auto loan. Understanding these factors is crucial for consumers seeking the most favorable financing options. Loan terms, including the loan duration and down payment amount, directly affect the interest rate and, ultimately, the total cost of the loan.Loan terms, such as the length of the loan and the amount of the down payment, are critical factors in determining the interest rate and the overall cost of the loan.
A shorter loan term generally translates to a lower total cost over the loan’s life. Conversely, a longer loan term, while potentially offering lower monthly payments, will increase the total interest paid. Down payments play a similar role, with larger down payments often leading to lower interest rates.
Impact of Loan Duration on Auto Loan Rates
Loan duration, or the length of time it takes to repay the loan, directly impacts the interest rate and the total cost of borrowing. Shorter loan terms usually result in lower interest rates because lenders perceive a lower risk of default over a shorter period. Conversely, longer loan terms often come with higher interest rates due to the increased risk associated with a longer repayment period.
This relationship is reflected in the total interest paid over the loan’s lifetime.
Impact of Down Payment on Auto Loan Rates
A larger down payment demonstrates the borrower’s financial stability and reduces the amount of principal the lender needs to finance. Lenders perceive this as a lower risk, resulting in lower interest rates and potentially lower monthly payments. The lower principal balance also leads to a reduced total interest paid over the loan’s life.
Comparison of Loan Terms and Total Loan Costs
The following table illustrates the impact of various loan terms on the total cost of a hypothetical $25,000 auto loan.
| Loan Term (Years) | Down Payment (%) | Interest Rate (%) | Total Loan Cost |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | 10% | 6.5% | $2,875 |
| 5 | 10% | 7.0% | $4,375 |
| 7 | 10% | 7.5% | $5,875 |
| 3 | 20% | 6.0% | $2,475 |
| 5 | 20% | 6.5% | $3,775 |
| 7 | 20% | 7.0% | $5,275 |
Calculation Methodology: The total loan cost is calculated by summing the total interest paid over the loan term. Interest is calculated using the following formula: Total Interest = Principal
- Interest Rate
- Loan Term (in years)
The table demonstrates how a larger down payment and a shorter loan term contribute to a lower total loan cost. The difference in interest rates and the resulting total loan costs highlight the importance of optimizing loan terms to minimize the overall cost of borrowing.
Government Policies and Their Influence
Government policies play a significant role in shaping the auto loan market. These policies, encompassing tax incentives, subsidies, and regulations, directly impact consumer demand, loan availability, and ultimately, interest rates. Understanding these influences is crucial for both consumers and lenders in anticipating future trends.
Impact of Tax Incentives on Electric Vehicles
Government tax incentives, such as tax credits for electric vehicles (EVs), can significantly stimulate consumer demand. These incentives often reduce the overall cost of purchasing an EV, making them more competitive with traditional gasoline-powered vehicles. As a result, increased demand can lead to a greater volume of loans for EV purchases. For example, the substantial tax credits offered in various countries have spurred the adoption of EVs, leading to increased production and demand for associated financing solutions.
Potential Impact of Subsidies on Loan Availability
Government subsidies for auto loans, while less common than tax incentives for specific vehicle types, can influence loan availability and rates. Such subsidies might target specific demographics or geographic regions. For example, a subsidy program aimed at encouraging EV adoption in rural areas could increase the demand for financing in those regions, prompting lenders to offer more financing options.
This could lead to more favorable loan terms, potentially lowering interest rates. However, the effectiveness of subsidies depends heavily on their design, implementation, and overall economic context.
Regulatory Changes and the Auto Loan Market
Potential regulatory changes impacting the auto loan market could include stricter lending standards or regulations concerning interest rate caps. For instance, new regulations aimed at combating predatory lending practices could influence the types of loans offered and potentially affect interest rates. These regulations can influence lending criteria, impacting both loan availability and the overall competitiveness of the market. Furthermore, stricter standards for loan origination, documentation, and risk assessment may require lenders to adjust their operational strategies.
Influence of Environmental Sustainability Policies
Government policies promoting environmental sustainability, such as regulations on emissions standards or incentives for the adoption of cleaner technologies, can significantly influence the auto loan market. Stricter emissions standards might encourage the adoption of hybrid or fully electric vehicles. This, in turn, could increase demand for these vehicles, potentially leading to more financing options and lower rates, as the market responds to the increased demand.
This shift could also lead to increased availability of financing options specifically targeted at sustainable transportation.
Alternative Financing Options
Beyond traditional auto loans, various alternative financing options offer different advantages and disadvantages for consumers. Understanding these alternatives allows individuals to make informed decisions aligning with their financial situations and goals. Choosing the right option depends on factors like creditworthiness, desired vehicle, and personal financial circumstances.
Comparison of Traditional Auto Loans, Leases, and Private Financing
Auto loans, leases, and private financing represent distinct approaches to acquiring a vehicle. Each option carries its own set of pros and cons, impacting the overall cost and ownership experience.
| Financing Type | Advantages | Disadvantages | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Auto Loan | Often lower monthly payments compared to leasing; ownership of the vehicle at the end of the loan term; potential for higher total cost depending on interest rates and loan terms. | Higher total cost if interest rates are high; responsibility for maintenance and repairs throughout the loan term. | Creditworthiness, loan terms, and prevailing interest rates are crucial factors. |
| Leasing | Lower monthly payments, often including insurance; less responsibility for maintenance and repairs (often handled by the leasing company); no ownership of the vehicle at the end of the lease term. | Vehicle’s value depreciates more quickly than a traditional loan; potentially higher total cost over the long term; mileage restrictions; potential penalties for exceeding mileage. | Mileage expectations, lease term, and the vehicle’s resale value are key aspects. |
| Private Financing | Potentially lower interest rates; negotiation power may be greater than with a traditional lender; greater flexibility in loan terms; potential for finding better rates if the borrower has strong bargaining power. | Increased risk of default; difficulty in obtaining financing; lack of recourse for issues with the vehicle. | Thorough vetting of the seller and careful consideration of the loan terms are paramount. |
Potential Emergence of New Financing Models in 2025
Several emerging models are expected to shape the auto financing landscape in 2025. These include subscription-based models, offering monthly payments for vehicle use, similar to streaming services, and fractional ownership schemes, allowing individuals to share ownership of a vehicle. Furthermore, fintech innovations may create entirely new platforms for auto financing, offering streamlined processes and potentially competitive rates. These new models might address specific consumer needs and preferences, providing alternative solutions beyond the traditional options.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, Auto Loan Rates 2025 presents a detailed forecast of the market, outlining potential trends and their underlying causes. The analysis provides a comprehensive view of the factors shaping borrowing costs for auto loans, offering valuable insights for consumers and financial institutions alike. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for informed decision-making in the automotive market.
FAQ Corner
What is the expected impact of inflation on auto loan rates in 2025?
Inflation’s impact on auto loan rates is complex. A higher inflation rate often leads to higher interest rates, increasing the cost of borrowing. However, the exact relationship depends on the interplay of various economic factors.
How will consumer confidence affect loan demand in 2025?
Consumer confidence plays a significant role in loan demand. Higher consumer confidence typically leads to increased borrowing, potentially boosting demand for auto loans. Conversely, low confidence can result in reduced demand.
What alternative financing options are available besides traditional auto loans?
Alternative financing options include leasing and private financing. Leasing involves paying for the use of a vehicle, while private financing allows individuals to secure loans from private lenders. Each option has its own advantages and disadvantages.
How do government policies influence auto loan rates?
Government policies, such as tax incentives for electric vehicles, can impact consumer demand and, consequently, auto loan rates. These policies can either encourage or discourage borrowing, depending on the specific incentive.




