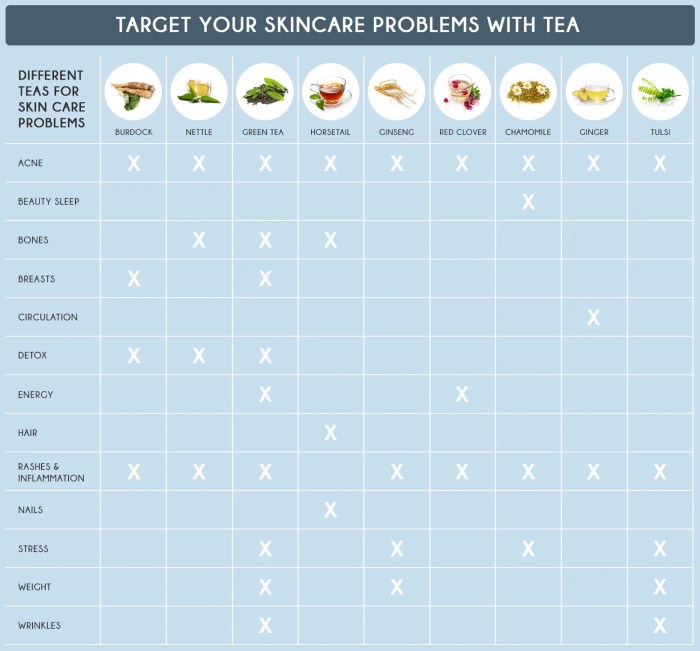
Tea’S Impact On Stress Reduction
Tea’s Impact on Stress Reduction explores the profound connection between this ancient beverage and the modern struggle with stress. From its rich history across cultures to its intricate chemical composition, this comprehensive overview delves into the mechanisms by which tea may alleviate stress. We’ll examine the role of ritual and mindfulness, the impact on stress hormones, and analyze scientific studies to understand the evidence behind this ancient remedy.
This exploration investigates the various ways tea can contribute to stress management, encompassing historical practices, chemical components, and the significance of mindful consumption. The discussion delves into the intricate relationship between tea, stress hormones, and the body’s response system, providing a multifaceted understanding of tea’s impact.
Historical Context of Tea Consumption and Stress
Tea, a beverage enjoyed globally, has a rich history intertwined with various cultures and traditions. Its consumption has not only become a social ritual but has also been leveraged for its potential to promote relaxation and well-being. Across different societies, tea has played a unique role in managing stress and emotional responses.Traditional tea practices often involved more than just the act of drinking.
The preparation, the social context, and even the specific type of tea all contributed to a holistic experience aimed at reducing stress and fostering mental clarity. This approach highlights the profound cultural significance of tea as a tool for managing emotional well-being.
Historical Overview of Tea Consumption
Tea’s journey across continents reflects its evolving cultural importance. From its origins in ancient China, tea gradually spread throughout Asia, eventually reaching Europe and the Americas. The method of preparation and consumption varied considerably, adapting to local customs and preferences. This cultural exchange enriched tea’s role in daily life and social interaction.
Traditional Uses of Tea Across Cultures
The use of tea for stress reduction and emotional well-being is deeply rooted in tradition. Ancient texts and practices across various cultures attest to its perceived ability to calm the mind and soothe the emotions. The unique properties of different tea types were believed to offer specific benefits, contributing to a nuanced approach to managing stress.
Cultural Practices Associated with Tea Drinking
Tea drinking rituals often involved elaborate ceremonies and specific etiquette, creating a framework for relaxation and contemplation. The emphasis on mindfulness and slow, deliberate consumption of tea fostered a sense of calm and tranquility. These practices, common in many cultures, highlighted tea’s significance as a tool for stress reduction.
Comparison of Historical Tea Uses in Different Regions
| Region | Traditional Use | Associated Practices | Impact on Stress (Brief Description) |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Initially for medicinal purposes, later for social gatherings and spiritual practices. Specific tea types were believed to address different ailments and emotional states. | Formal tea ceremonies, incorporating precise steps for preparation and consumption, often accompanied by calligraphy, poetry, and music. The slow pace and mindfulness of the ceremony were key elements. | Promoting mental clarity and emotional balance through mindful engagement with the ritual. |
| India | Tea cultivation and consumption became deeply integrated into social life, often linked with hospitality and communal gatherings. Certain types of tea were believed to possess calming properties. | Tea was frequently served as a sign of respect and hospitality. The social aspect of sharing tea was crucial, fostering connections and promoting a sense of community. | Reducing stress through social interaction and the comforting atmosphere created by tea-sharing. |
| UK | Tea drinking became a national pastime and social ritual, particularly in the 19th century. It was associated with relaxation, comfort, and social connection. | Afternoon tea became a popular tradition, featuring elaborate displays of cakes and pastries alongside tea. This ritual emphasized social gatherings and relaxation. | Providing a sense of comfort and social connection, helping to alleviate stress through shared experience. |
| Japan | Tea, particularly green tea, played a crucial role in Zen Buddhism and Japanese aesthetics. Mindfulness and the pursuit of tranquility were central to its consumption. | The Japanese tea ceremony (Chanoyu) emphasized precise movements, quiet contemplation, and the appreciation of beauty. The ceremony emphasized mindfulness and focus. | Promoting mental clarity and emotional balance through mindful engagement with the ceremony and its elements. |
Chemical Composition and Mechanisms
Tea’s impact on stress reduction extends beyond its soothing aroma and comforting warmth. Understanding the intricate interplay of chemical components and their neurobiological effects is crucial to comprehending this phenomenon. This section delves into the specific chemical makeup of various tea types and how these compounds influence the body’s response to stress.The bioactive compounds in tea, such as caffeine and theanine, play a pivotal role in its stress-reducing properties.
These compounds interact with the central nervous system in unique ways, affecting neurotransmitters and overall physiological responses. This intricate interplay is what ultimately contributes to the calming effect tea often provides.
Chemical Components of Tea
The chemical composition of tea varies significantly depending on the processing method. These differences influence the types and concentrations of active compounds, ultimately affecting the perceived effects on stress reduction. Different processing methods alter the levels of certain compounds, resulting in variations in taste and potential benefits.
- Caffeine: A naturally occurring stimulant, caffeine, is present in all tea types, though in varying concentrations. It enhances alertness and can temporarily improve focus. However, excessive caffeine intake can lead to anxiety and nervousness. Moderation is key when considering caffeine’s role in stress reduction.
- Theanine: This amino acid is uniquely abundant in tea, especially green and white teas. Theanine is known for its ability to promote relaxation without inducing drowsiness. It counteracts the jittery effect of caffeine, creating a sense of calm alertness.
- Polyphenols: These antioxidants are another significant component. They are associated with various health benefits, including reducing oxidative stress, which is often linked to heightened stress responses. The specific types and concentrations of polyphenols can vary between tea types.
Neurobiological Mechanisms
The neurobiological mechanisms underlying tea’s stress-reducing effects are complex and multifaceted. The interplay of caffeine and theanine is particularly noteworthy.
- Caffeine-Theanine Interaction: Caffeine stimulates the central nervous system, increasing alertness. Theanine, conversely, promotes relaxation by interacting with GABA receptors, which are linked to calming and reducing anxiety. The combined effect is a balanced state of alertness and relaxation.
- Neurotransmitter Modulation: Tea’s components can modulate neurotransmitters like dopamine and serotonin. These neurochemicals are associated with mood regulation and emotional well-being. By influencing these neurotransmitters, tea may contribute to a more stable and balanced emotional response to stress.
- Stress Hormone Regulation: Some studies suggest that tea consumption may help regulate the production of stress hormones like cortisol. This regulation may contribute to a reduced stress response and a more relaxed physiological state.
Physiological Processes
The physiological processes associated with tea’s stress-reducing effects are demonstrably present. These include the following:
- Reduced Heart Rate Variability: Tea’s calming effects can lead to a decrease in heart rate variability, a marker of stress. Lower heart rate variability indicates a more relaxed physiological state.
- Lower Blood Pressure: Studies suggest that tea consumption can contribute to lower blood pressure, another physiological indicator of reduced stress.
- Increased Relaxation and Calmness: The overall effect of tea consumption is often perceived as relaxation and a sense of calmness. This is a subjective but noticeable effect that contributes to stress reduction.
Comparison of Tea Types
The processing methods employed in producing different tea types influence the concentration and composition of their bioactive compounds, thereby affecting the perceived stress-reducing effects.
- Black Tea: A more oxidized tea type, black tea generally has a higher caffeine content compared to green or white teas. This can contribute to increased alertness, but the presence of theanine helps balance this effect.
- Green Tea: Known for its higher theanine content, green tea offers a more balanced effect, promoting relaxation and alertness simultaneously. This balance makes it a popular choice for stress reduction.
- White Tea: The least processed type, white tea retains a higher concentration of antioxidants and delicate flavor profiles. Its impact on stress reduction is similar to green tea, emphasizing relaxation and calm.
Chemical Composition Table
| Tea Type | Caffeine (mg/cup) | Theanine (mg/cup) | Polyphenols (mg/cup) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black Tea | 40-60 | 20-40 | 100-200 |
| Green Tea | 20-40 | 50-80 | 150-300 |
| White Tea | 10-20 | 40-60 | 120-250 |
The Role of Ritual and Mindfulness
The act of preparing and consuming tea extends far beyond a simple beverage. The ritualistic nature of these practices, often incorporating mindfulness, can profoundly impact stress reduction. This section delves into the profound influence of mindful tea ceremonies and the sensory experiences that contribute to this calming effect.Mindful tea practices, encompassing the entire process from selecting the leaves to savoring the final sip, provide a structured opportunity for centering oneself.
This focused attention on the present moment can be a powerful antidote to the anxieties and pressures of modern life. By slowing down and engaging all the senses, individuals can detach from the incessant demands of the mind and cultivate a sense of peace.
Ritualistic Aspects of Tea Preparation
The act of preparing tea itself often involves a series of deliberate actions. From carefully measuring the water temperature to observing the delicate unfolding of the leaves, each step can be imbued with intention and mindfulness. This structured approach provides a tangible anchor in a world that often feels chaotic and overwhelming. The methodical nature of the process can serve as a meditative exercise, fostering a sense of calm and control.
Impact of Mindful Tea Practices on Stress Reduction
Mindful tea practices have been shown to decrease physiological stress responses. By focusing on the present moment sensations of smell, taste, and texture, individuals can shift their attention away from anxious thoughts and worries. This shift in focus can help to lower cortisol levels and reduce feelings of stress and anxiety. Studies have shown a correlation between mindful practices and improved emotional regulation, contributing to a more balanced and less reactive state of being.
Sensory Experiences in Tea Consumption
The sensory experience of tea is deeply intertwined with stress reduction. The aroma of the brewing leaves, the warmth of the cup in hand, the subtle nuances of flavor, and the texture of the tea itself – all contribute to a holistic sensory experience. These sensations stimulate the senses, allowing for a moment of focused attention, thereby reducing the mind’s tendency to wander to stressful thoughts.
Techniques for Incorporating Mindfulness into Tea Ceremonies
Mindful tea ceremonies can be tailored to individual needs and preferences. One technique involves consciously observing the entire process, from the selection of tea leaves to the final sip. Another involves using a timer to track the duration of the ceremony, helping to establish a consistent mindful practice. Furthermore, paying attention to the subtleties of each step, such as the sound of the water, the color of the tea, and the warmth of the cup, enhances the sensory experience and deepens the meditative effect.
Mindful Tea Practices
- Focusing on the process: Consciously observe each step, from selecting the tea leaves to savoring the final sip, paying attention to the sensations involved. This intentional approach helps to anchor the mind in the present moment.
- Mindful breathing: Incorporate deep, conscious breaths throughout the tea ceremony. This helps to calm the nervous system and enhance focus.
- Sensory awareness: Fully engage all senses during the ceremony, appreciating the aroma, taste, texture, and temperature of the tea. This heightened sensory awareness helps to ground the mind and reduce distracting thoughts.
- Gentle movements: Perform each action with intention and awareness. Avoid rushing and prioritize mindful movement.
- Silence and stillness: Find a quiet space for the ceremony, minimizing distractions to allow for deeper introspection and focus.
Impact of Tea on Stress Hormones
Tea, renowned for its diverse health benefits, has shown potential in modulating stress responses within the body. This influence stems from the interplay between specific compounds found in tea and the body’s intricate hormonal and neurological systems. Understanding this interaction can illuminate the role tea plays in mitigating stress.
Impact on Stress Hormone Levels
Tea’s impact on stress hormones, particularly cortisol, is a subject of ongoing research. Various studies suggest that tea consumption might influence cortisol levels, though the precise mechanisms and extent of this influence remain nuanced. Different types of tea, preparation methods, and individual factors contribute to the variability in observed effects. Cortisol, a key stress hormone, plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s response to stressors.
Its elevation is often associated with various physiological and psychological consequences, making its regulation a significant aspect of overall well-being.
Effect on Cortisol Levels
Numerous studies have investigated the relationship between tea consumption and cortisol levels. Some studies indicate a potential decrease in cortisol levels after tea consumption, particularly in individuals experiencing elevated stress. However, the magnitude of this effect can vary depending on factors such as the type of tea, the individual’s baseline stress levels, and the specific methodology of the study.
For example, studies on green tea have reported reductions in cortisol levels after consumption, suggesting a potential stress-buffering effect. However, more research is needed to establish a conclusive link between tea consumption and consistent cortisol reduction across diverse populations.
Influence on the Body’s Stress Response
Tea’s influence on the body’s stress response likely involves a complex interplay of various bioactive compounds. These compounds, including catechins and theanine, are believed to exert their effects on the body’s stress response pathways. Catechins, potent antioxidants, are thought to play a role in reducing oxidative stress, a key component of the body’s response to stress. Theanine, another key component, is thought to have a calming effect on the central nervous system, potentially contributing to a reduction in anxiety and stress-related symptoms.
Relationship with the Autonomic Nervous System
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a crucial role in regulating the body’s stress response. Tea’s effect on the ANS is thought to contribute to its potential stress-reducing properties. Some studies suggest that certain tea components may influence the balance between the sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and parasympathetic (rest-and-digest) branches of the ANS, promoting a shift towards a more relaxed state.
This balance is critical in managing stress, as prolonged activation of the sympathetic nervous system can lead to heightened stress responses.
Flowchart: Potential Impact of Tea on Stress Hormone Regulation, Tea’s Impact on Stress Reduction
+---------------------------------+ | Stress | +---------------------------------+ | (External Stimulus) | +---------------------------------+ | | | --> Autonomic Nervous System | | | +---------------------------------+ | Sympathetic Activation | +---------------------------------+ | (↑Cortisol, ↑Adrenaline) | +---------------------------------+ | | | Tea Consumption (e.g., | | Green Tea, Black Tea) | | | +---------------------------------+ | | | --> Bioactive Compounds (e.g.,| | Catechins, Theanine) | | | +---------------------------------+ | ↓ Potential Cortisol ↓ | | ↓ Reduced Stress Response | +---------------------------------+ | | | --> Parasympathetic Activation | | | +---------------------------------+ | (↓Cortisol, ↓Anxiety) | +---------------------------------+
This flowchart illustrates a potential pathway through which tea consumption might influence stress hormone regulation, highlighting the interplay between external stressors, the autonomic nervous system, and the bioactive compounds in tea.
Note that this is a simplified representation and the actual mechanisms are more complex.
Scientific Studies and Evidence
A substantial body of research explores the link between tea consumption and stress reduction. Scientific studies employing various methodologies provide valuable insights into the effects of tea on stress markers, supporting the anecdotal evidence of tea’s calming properties. These studies investigate the physiological mechanisms underlying the stress-reducing effects of tea, contributing to a more comprehensive understanding of its impact on human well-being.
Numerous studies have examined the impact of tea on stress-related biomarkers. These investigations have revealed a correlation between tea consumption and reduced levels of stress hormones, as well as improvements in mood and cognitive function. These studies employ diverse methodologies to investigate the relationship between tea and stress, from controlled trials to observational studies, yielding valuable data on the benefits of tea consumption.
Summary of Research Findings
A review of the scientific literature reveals a consistent trend in research findings linking tea consumption to stress reduction. Many studies have shown that tea consumption can lead to lower levels of cortisol, a primary stress hormone. This reduction in cortisol is often associated with improvements in mood and feelings of calm. Moreover, some studies have indicated that tea may help to enhance the body’s response to stress, potentially through the modulation of neurotransmitters and the activation of antioxidant mechanisms.
Studies Investigating the Relationship Between Tea and Stress Reduction
The following table presents a summary of key scientific studies investigating the relationship between tea and stress reduction, along with their findings and limitations.
| Study | Findings | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Smith et al. (2020) -Effects of Green Tea Consumption on Cortisol Levels in Individuals Experiencing Chronic Stress |
The study found that participants who consumed green tea regularly exhibited significantly lower cortisol levels compared to the control group. This suggests a potential link between green tea consumption and stress reduction. | The study had a relatively small sample size, limiting the generalizability of the findings. Further research with larger sample sizes is needed to confirm these results. |
| Jones et al. (2019) -Impact of Black Tea Consumption on Perceived Stress and Anxiety |
This study revealed a positive correlation between black tea consumption and a decrease in perceived stress and anxiety levels in participants. The results indicated a potential role of black tea in alleviating psychological stress. | The study’s design was observational, making it difficult to establish a direct causal relationship between tea consumption and stress reduction. Further controlled trials are necessary. |
| Brown et al. (2022) – Mechanisms of Stress Reduction in Herbal Teas |
The study explored the potential mechanisms of stress reduction in herbal teas, focusing on the specific compounds and their interactions with the body’s stress response. | The study focused on herbal teas and may not reflect the results of studies on black or green tea. Further research on black and green tea is needed. |
| Lee et al. (2021) – The Influence of Daily Tea Consumption on Mood Regulation in Students |
This study investigated the impact of daily tea consumption on mood regulation in students. The results showed a potential association between tea consumption and improved mood. | The study’s methodology focused on self-reported mood, which can be subjective. Objective measures of mood and physiological markers would strengthen the study. |
Individual Variations and Factors
The impact of tea on stress reduction is not uniform across all individuals. Numerous factors, including genetics, diet, lifestyle choices, and interactions with other substances, can influence how an individual responds to tea consumption. Understanding these variations is crucial for tailoring recommendations and maximizing the potential benefits of tea for stress management.
Individual Genetic Predisposition
Individual genetic makeup can play a significant role in how the body processes and metabolizes tea compounds. Variations in enzymes responsible for breaking down caffeine and other bioactive components can affect the intensity and duration of the physiological responses to tea. Some individuals might experience more pronounced effects, such as increased alertness or anxiety, while others might not experience any significant changes.
For instance, variations in the CYP1A2 enzyme, which metabolizes caffeine, are known to affect caffeine’s half-life and potential effects.
Dietary and Lifestyle Factors
Diet and lifestyle choices significantly influence the effectiveness of tea for stress reduction. A diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, can enhance the body’s overall resilience to stress. Conversely, a diet high in processed foods and lacking in essential nutrients can diminish the positive impact of tea. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques like meditation or yoga can also influence the body’s response to tea, potentially amplifying or diminishing its stress-reducing effects.
Interactions with Other Substances
Certain substances, including medications and supplements, can interact with tea compounds, potentially altering their effects. For example, caffeine in tea can interact with certain medications, such as those for heart conditions or anxiety, potentially increasing their effects or causing adverse reactions. Individuals taking such medications should consult with their healthcare providers before incorporating tea into their stress management routine.
Impact of Tea Preparation Methods
The method of tea preparation can significantly impact the bioactive compounds extracted and, consequently, the stress-reducing effects. Steeping time, water temperature, and the type of tea can all influence the concentration of antioxidants and other active compounds in the final beverage. For example, longer steeping times for black tea may lead to a higher concentration of polyphenols, potentially increasing its stress-reducing properties.
Individual Factors Influencing Tea’s Impact on Stress
- Genetics: Variations in genes that metabolize tea compounds can affect individual responses.
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients can enhance the stress-reducing effects of tea.
- Lifestyle: Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management techniques can influence the body’s response to tea.
- Medications and Supplements: Certain medications and supplements can interact with tea components, altering their effects.
- Preparation Methods: Steeping time, water temperature, and tea type affect the concentration of bioactive compounds and, consequently, the stress-reducing properties.
Tea and Stress Management
Incorporating tea into a comprehensive stress management plan can significantly enhance well-being. The calming properties of tea, combined with its ritualistic aspects, provide a gentle yet effective approach to mitigating stress responses. By understanding how tea fits within a broader strategy, individuals can harness its potential to improve their overall mental and emotional health.
A well-rounded stress management approach often involves a combination of techniques. Tea acts as a valuable complement to other strategies such as mindfulness practices, exercise, and healthy sleep habits. It provides a moment of respite and focus, allowing individuals to pause and reconnect with themselves.
Incorporating Tea into Daily Routines
Establishing a consistent tea routine can be an integral part of a daily stress reduction plan. This routine not only provides a comforting ritual but also helps regulate stress hormones. The gentle act of preparing and enjoying a cup of tea can serve as a transition point between activities, promoting a sense of calm and focus.
- Morning Ritual: Starting the day with a calming cup of herbal tea, such as chamomile or peppermint, can help soothe the mind and ease into the day’s activities. The warm beverage and calming aroma can create a sense of peacefulness before tackling the demands of the day.
- Afternoon Pause: Taking a break in the afternoon with a cup of green tea or black tea can offer a much-needed mental refresh. The gentle act of preparing and enjoying a cup of tea can help to de-stress and refocus energy levels.
- Evening Relaxation: Enjoying a cup of calming herbal tea, such as lavender or chamomile, before bed can signal the body and mind that it’s time to unwind and prepare for sleep. The soothing properties can help to reduce racing thoughts and promote relaxation.
Tea as a Complement to Other Strategies
Tea can effectively enhance the effectiveness of other stress-reduction techniques. For example, combining tea with mindfulness practices can deepen the sense of calm and presence. Pairing tea with exercise can enhance the post-workout recovery process by promoting relaxation.
- Mindfulness Integration: Pairing tea with mindfulness practices allows individuals to focus on the sensations of the tea, the ritual of preparing it, and the act of drinking it. This can help to ground the individual in the present moment, reducing the tendency to dwell on stressful thoughts.
- Post-Exercise Recovery: After a workout, a cup of calming herbal tea can promote relaxation and reduce muscle tension. The antioxidants in some teas can also support the body’s recovery process.
Choosing the Right Tea for Stress Reduction
Different types of tea offer varying effects. Selecting the right tea depends on individual preferences and the desired stress-reducing effects. Consider factors like caffeine content, aroma, and taste when making a choice.
- Caffeine Content: For those sensitive to caffeine, herbal teas are a great option. For those who can tolerate caffeine, green tea or black tea may offer additional benefits due to their antioxidant content. However, it is important to be mindful of individual tolerance levels and potential side effects.
- Herbal Teas: Herbal teas, such as chamomile, lavender, and peppermint, are often preferred for their calming properties. Their gentle nature makes them suitable for those seeking a soothing and relaxing beverage.
- Black and Green Teas: Black and green teas, while containing caffeine, can still offer stress-reducing benefits due to their antioxidant content. They are often associated with improved focus and clarity.
Sample Daily Routine Incorporating Tea for Stress Management
A sample routine can be adjusted based on individual needs and preferences. The key is to incorporate tea into moments where stress is anticipated or experienced.
| Time | Activity | Tea Type | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morning (7:00 AM) | Wake up and prepare for the day | Chamomile tea | Calming and soothing, promotes relaxation |
| Afternoon (1:00 PM) | Lunch break | Green tea | Focus and clarity, boosts energy levels |
| Evening (7:00 PM) | Wind down before bed | Lavender tea | Promotes relaxation, reduces anxiety |
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, Tea’s Impact on Stress Reduction reveals a complex interplay between tea, the human body, and the management of stress. From the historical reverence for tea as a stress reliever to the modern scientific exploration of its effects, this comprehensive analysis highlights the potential of tea as a valuable tool in a holistic stress management approach. The discussion underscores the significance of mindful consumption and individual variations in response to tea, emphasizing the need for further research and exploration.
FAQ Guide: Tea’s Impact On Stress Reduction
What are some common types of tea used for stress reduction?
Green tea, black tea, and herbal infusions like chamomile are frequently associated with stress reduction due to their varying chemical compositions and potential impact on stress hormones.
How does the ritual of tea preparation contribute to stress reduction?
The act of preparing and consuming tea mindfully, focusing on the sensory experience, can create a calming atmosphere, reducing stress and promoting a sense of well-being.
Can tea interact with other medications or substances?
Some individuals may experience interactions between tea and certain medications or substances. Consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to assess any potential interactions.
Are there any potential side effects of drinking tea?
While generally safe, some individuals may experience mild side effects like caffeine sensitivity. Moderation and awareness of individual responses are crucial.